Vitamin B6 foods, also known as pyridoxine, is an essential nutrient that plays a vital role in maintaining overall health. It is involved in various bodily functions, such as metabolism, brain development, and immune system support. Because the body cannot store vitamin B6, it is crucial to obtain it regularly through your diet. This article explores the importance of vitamin B6, its benefits, and the best food sources to include in your daily meals.
The Role of Vitamin B6 in the Body
Vitamin B6 is a water-soluble vitamin that is crucial for numerous physiological functions:
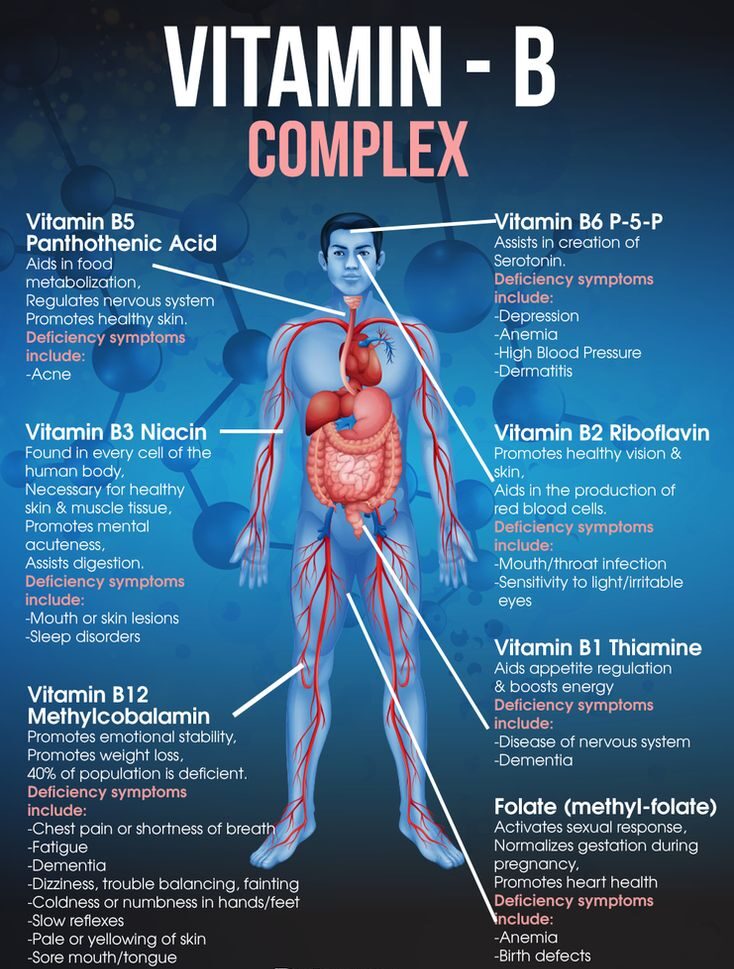
Vitamin B6 Foods ,Vitamin B6 acts as a coenzyme in many enzyme reactions related to the metabolism of proteins, carbohydrates, and fats. It is vital for converting food into energy, synthesizing neurotransmitters, and producing hemoglobin.
Brain Development and Function: It plays a key role in cognitive development by aiding in the production of neurotransmitters, the chemicals that transmit signals in the brain. Adequate vitamin B6 levels are linked to improved mood, memory, and a lower risk of cognitive decline.
Immune System Support: Vitamin B6 Foods is involved in the synthesis of antibodies and cytokines, which are essential for a healthy immune response. It helps the body fight infections and maintain immune health.
Hormonal Balance: Vitamin B6 helps regulate hormones, particularly in women. It can alleviate symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) by regulating serotonin and dopamine, which influence mood and behavior.
Cardiovascular Health: By helping to regulate homocysteine levels—a risk factor for heart disease—vitamin B6 plays a protective role in maintaining cardiovascular health. Elevated homocysteine can lead to artery damage, so maintaining adequate levels of vitamin B6 can reduce this risk.
Daily Requirements of Vitamin B6
The recommended daily intake of vitamin B6 varies depending on age, gender, and life stage. Here’s a breakdown:
- Infants (0-12 months): 0.1 to 0.3 mg per day
- Children (1-8 years): 0.5 to 0.6 mg per day
- Adolescents (9-18 years): 1.0 to 1.3 mg per day
- Adults (19-50 years): 1.3 mg per day
- Men (51 years and older): 1.7 mg per day
- Women (51 years and older): 1.5 mg per day
- Pregnant Women: 1.9 mg per day
- Breastfeeding Women: 2.0 mg per day
Top Vitamin B6-Rich Foods
Ensuring adequate intake of Vitamin B6 Foods is possible through a varied diet that includes different food groups. Here are some of the best sources:
1. Poultry
Chicken: Chicken breast is one of the richest sources of vitamin B6, offering approximately 0.5 mg per 3-ounce serving. It’s a versatile protein that can be used in a variety of dishes, from salads to soups and main courses.
Turkey: A 3-ounce serving of turkey contains around 0.4 mg of vitamin B6. Turkey is not only a great source of this vitamin but also provides high-quality protein, making it an excellent choice for those looking to build muscle or maintain a healthy diet.
2. Fish

Salmon: This fatty fish is rich in vitamin B6, providing about 0.6 mg per 3-ounce serving. Salmon is also packed with omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential for heart and brain health.
Tuna: Both fresh and canned tuna are high in vitamin B6, with a 3-ounce serving offering approximately 0.9 mg. Tuna is a lean protein that’s perfect for sandwiches, salads, and main dishes.
Halibut: Halibut provides about 0.4 mg of vitamin B6 per serving and is a low-fat option that’s rich in nutrients. It’s an excellent addition to a heart-healthy diet.
3. Beans and Legumes
Chickpeas (Garbanzo Beans): A cup of cooked chickpeas delivers about 1.1 mg of vitamin B6. They are versatile and can be used in salads, stews, or made into hummus.
Lentils: Lentils offer around 0.4 mg of vitamin B6 per cup. They are a nutrient-dense food, providing fiber, protein, and essential vitamins, making them a staple in vegetarian diets.
Pinto Beans: One cup of cooked pinto beans contains approximately 0.6 mg of vitamin B6. Pinto beans are great in soups, stews, and as a filling for tacos and burritos.
4. Nuts and Seeds

Sunflower Seeds: These seeds are an excellent source of vitamin B6, providing about 0.4 mg per 1-ounce serving. They make a great snack and can be added to salads and baked goods.
Walnuts: Walnuts contain about 0.2 mg of vitamin B6 per 1-ounce serving. They are also rich in omega-3 fatty acids and make a healthy addition to your diet.
Hazelnuts: Hazelnuts offer around 0.2 mg of vitamin B6 per 1-ounce serving and are a delicious option for snacking or baking.
5. Whole Grains
Brown Rice: A cup of cooked brown rice provides about 0.3 mg of vitamin B6. Brown rice is a whole grain that is also rich in fiber and other essential nutrients.
Oatmeal: Oats are a good source of vitamin B6, with a cup of cooked oatmeal offering approximately 0.1 mg. They are a healthy breakfast option that can help maintain energy levels throughout the day.
Quinoa: Quinoa contains about 0.2 mg of vitamin B6 per cooked cup. This ancient grain is also high in protein and can be used in salads, soups, or as a side dish.

6. Fruits

Bananas: Bananas are well-known for their vitamin B6 content, with one medium banana providing about 0.4 mg. They are an easy, portable snack that also offers fiber and potassium.
Avocados: Avocados contain about 0.5 mg of vitamin B6 per medium fruit. They are also rich in healthy fats and can be used in salads, sandwiches, or as a spread.
Prunes: Dried prunes provide around 0.2 mg of vitamin B6 per cup and are an excellent source of fiber. They can be added to cereals, salads, or eaten as a snack.
7. Vegetables
Spinach: Spinach is a leafy green that is high in vitamin B6 and other essential nutrients. A cup of cooked spinach provides about 0.2 mg of vitamin B6. It can be added to smoothies, salads, and cooked dishes.
Potatoes: Potatoes, especially when eaten with the skin, are a good source of vitamin B6. A medium potato offers approximately 0.4 mg of vitamin B6 and can be prepared in various ways, including baking, roasting, or mashing.
Carrots: Carrots provide about 0.2 mg of vitamin B6 per cup of sliced carrots. They are also rich in beta-carotene, which supports vision health. Carrots can be eaten raw, cooked, or blended into soups and smoothies.

Health Benefits of Vitamin B6
Ensuring adequate intake of vitamin B6 offers numerous health benefits:
Mood Regulation and Reduced Depression Symptoms: Vitamin B6 is vital for the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin and dopamine, which regulate mood. Adequate B6 levels are associated with reduced symptoms of depression and anxiety, making it an essential nutrient for mental health.
Cognitive Function and Brain Health: Vitamin B6 contributes to brain health by supporting cognitive functions such as memory, focus, and processing speed. Research suggests that B6 may help reduce the risk of cognitive decline as we age.
Cardiovascular Health: By helping to regulate homocysteine levels—a risk factor for heart disease—vitamin B6 plays a protective role in cardiovascular health. Lowering homocysteine can reduce the risk of arterial damage and support overall heart health.
Immune System Enhancement: Vitamin B6 supports the immune system by aiding in the production of antibodies and cytokines, essential components of the body’s defense mechanisms. A strong immune system is crucial for fighting infections and maintaining overall health.
Hormonal Balance and PMS Relief: Vitamin B6 helps regulate hormonal activity, particularly in women. It can alleviate symptoms of premenstrual syndrome (PMS) by managing serotonin and dopamine levels, which influence mood and behavior.
Incorporating Vitamin B6 Foods into Your Diet
Here are some practical tips to help you incorporate vitamin B6-rich foods into your daily diet:
Plan Balanced Meals: Create meal plans that feature a combination of vitamin B6-rich foods, such as chicken, salmon, lentils, and spinach. This will ensure that you’re meeting your daily B6 requirements through a variety of food sources.
Snack Wisely: Choose snacks that are high in vitamin B6. For instance, munch on sunflower seeds or walnuts during the day, or grab a banana or avocado as a quick, nutrient-rich snack.
Include B6-Rich Foods at Breakfast: Start your day with oatmeal topped with sunflower seeds and a sliced banana, or opt for scrambled eggs with spinach and avocado on the side. These choices will help you get a strong start to your daily vitamin B6 intake.
Add More Beans and Legumes to Your Diet: Whether it’s a chickpea salad for lunch or a lentil stew for dinner, beans and legumes are rich in vitamin B6 and fiber, making them both filling and nutritious.
Incorporate Fish into Your Meals: Adding fish such as salmon, tuna, or halibut to your weekly meal plan will not only boost your vitamin B6 intake but also provide you with beneficial omega-3 fatty acids.
Mix It Up with Whole Grains: Opt for whole grains such as brown rice and quinoa as part of your main dishes. These grains offer vitamin B6 and help provide lasting energy throughout the day.
Use Potatoes and Carrots Creatively: Roasted potatoes or mashed carrots are both great side dishes and provide an easy way to incorporate more vitamin B6 into your diet.

Conclusion
Vitamin B6 plays a critical role in numerous bodily functions, from energy metabolism to brain function and immune health. Ensuring that you consume enough vitamin B6 through a well-balanced diet that includes foods such as poultry, fish, beans, seeds, nuts, and leafy greens is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. By making small, intentional choices, you can easily integrate these vitamin B6-rich foods into your meals, supporting your body’s need for this vital nutrient. Prioritizing a balanced and varied diet will help you meet your nutritional needs and enjoy the numerous health benefits of vitamin B6.